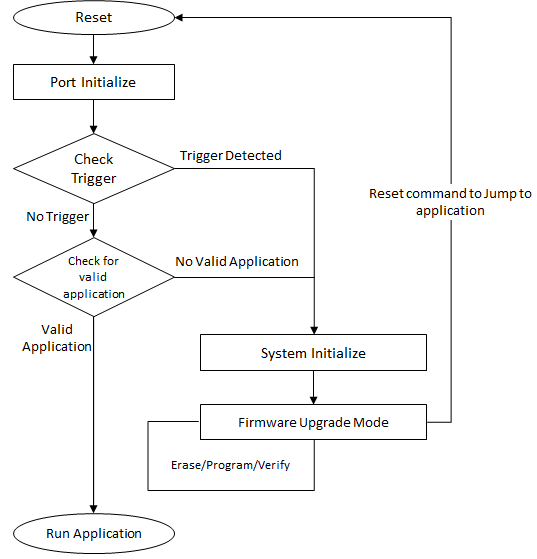
1.4.2 CAN Bootloader system level execution flow
Basic Bootloader system level execution flow
The Bootloader code starts executing on a device Reset
If there are no conditions to enter the firmware upgrade mode, the Bootloader starts executing the user application
Refer to Bootloader Trigger Methods for different conditions to enter firmware upgrade mode
The Bootloader performs Flash erase/program operations while in the firmware upgrade mode
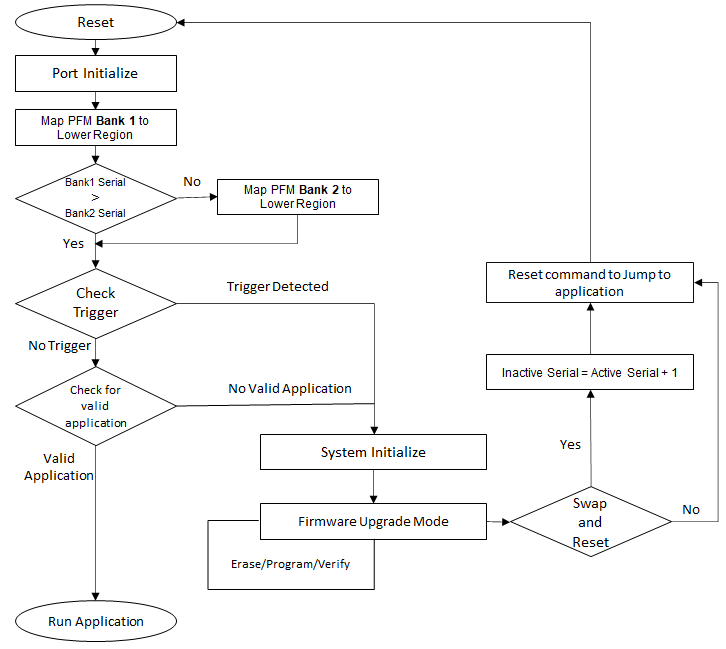
Fail Safe Update Bootloader system level execution flow (MIPS Based MCUs)
Bootloader always maps Bank 1 to lower region at boot up irrespective of cause for reset (Hard/Soft).
This is required because if Swap bit was set and a soft reset was triggered the value is retained but if Swap bit was set and Hard reset was triggered the value is cleared
Once Swap bit is cleared and Bank 1 is mapped to lower region it performs below operation
If Bank 1 serial number is greater than Bank 2 serial number it just continues for trigger check or runs application from Bank 1, As Bank 1 is already mapped to lower region in above step (Bank 1 is Active Bank)
If Bank 2 serial number is greater than Bank 1 serial number it maps Bank 2 to lower region by setting the Swap bit and proceeds to trigger check or runs application from Bank 2 (Bank 2 is Active Bank)
Whenever Bootlader programs new application in the Inactive bank and swap bank command is received it reads the serial number from Active bank, increments by 1 and then writes to Inactive Bank serial
Inactive Bank Serial number = Active Bank serial number + 1
Start address of inactive bank is equal start of mid of flash
If the Host application requests to update the Active Bank and the address falls into the active bank serial sector it sends an error response and aborts the programming operation