1.1 I2C EEPROM Bootloader
This example application shows how to use the Serial Memory Bootloader Library to bootload an application from I2C EEPROM (AT24) to Internal Flash.
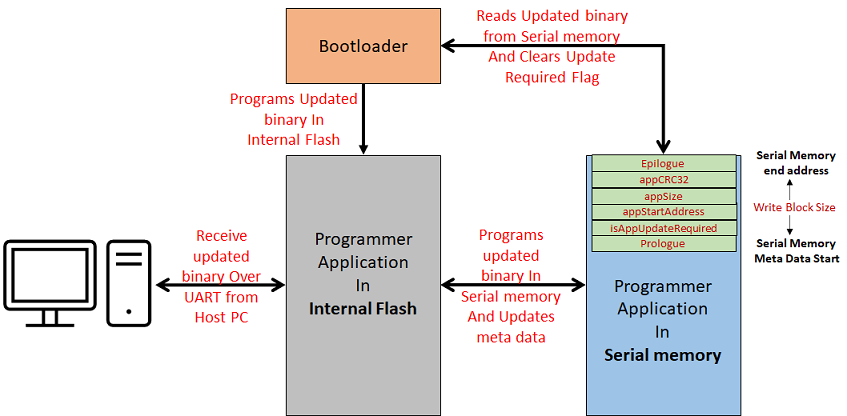
Serial Memory Bootloader Applications Block Diagram
Bootloader Application
This is a bootloader application which resides from
The starting location of the flash memory region for SAM devices
Performs Below Operation:
Sets up the I2C EEPROM (AT24) using the AT24 Driver
Checks if a firmware update is required by reading the MetaData stored in the last sector of I2C EEPROM
If Firmware update is required then it jumps to Step 4
If there was no firmware update request through MetaData, then it checks for any trigger implemented in application main()
Here we use the On-board Switch to force trigger firmware update.
If no trigger is found then it jumps to Step 7
If firmware update is required then it
Reads the programmer application binary stored from start of I2C EEPROM (0x0)
Programs the read binary to application space in Internal Flash
Once programming is done it generates a CRC32 value over programmed space and verifies it against the CRC32 stored in I2C EEPROM MetaData
If CRC32 verification fails it goes into Error State
If CRC32 verification is successful, It clears the firmware update required flag in the I2C EEPROM MetaData and triggers a Soft Reset
After reset, bootloader starts from Step 1 through Step 3 to do firmware update check and then jump to Step 7
If there was no firmware update required then it
Calls the SYS_Deinitialize() function which releases the resources used. This Function is device specific and has to be implemented based on application requirement
Jumps to application space to run the programmer application
Programmer Application
This is a I2C EEPROM programmer application which resides from
The end of bootloader size in device flash memory for SAM devices
It will be loaded into internal flash memory from I2C EEPROM by bootloader application
It blinks an LED every 500Ms and has capabilty to program I2C EEPROM (AT24) using AT24 Driver
It uses the Virtual Com port of the device (EDBG port or External USB to UART converters) to receive the binary to be programmed in I2C EEPROM from host PC
As the application running in internal flash should have capability to program I2C EEPROM, we send the programmer application binary itself via UART to be programmed in I2C EEPROM
It calls the APP_INPUT_Tasks() function which receives the binary to be programmed into I2C EEPROM over UART channel
It uses the UART bootloader protocol but is updated to run along with other tasks
Once the binary is received and programmed from start location of I2C EEPROM it generates a CRC32 value over programmed I2C EEPROM space and verifies it against the CRC32 sent from host PC
It Also Updates the CRC32 value received in the I2C EEPROM MetaData used by bootloader
If CRC32 verification fails it goes into Error State then resets the APP_INPUT_Tasks() state to receive new binary
If verification is successful then it
Waits for one of below user event to update the MetaData and trigger bootloader via soft reset to program new binary in Internal Flash OR
A Switch press OR
A Reboot command from Host PC
Waits for a new binary to be programmed in I2C EEPROM.
Development Kits The following table provides links to documentation on how to build and run I2C EEPROM bootloader on different development kits
